List of modern Russian small arms and light weapons

Multi tool use
List of modern Russian small arms and light weapons
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The following is a list of modern Russian small arms and light weapons which were in service in 2016:
Contents
1 Handguns
1.1 Revolvers
1.2 Pistols
1.3 Special purpose
2 Submachine guns
2.1 Special purpose
3 Shotguns
4 Rifles
4.1 Bolt-action
4.2 Semi-automatic
4.3 Selective-fire
4.4 Special purpose
4.5 Anti-material rifles
5 Machine guns
5.1 Squad automatic weapons (SAWs)
5.2 General-purpose
5.3 Heavy
6 Hand grenades
6.1 Fragmentation
6.2 Anti-tank
7 Grenade launchers
7.1 Stand-alone
7.2 Attached
7.3 Automatic grenade launchers
8 Rocket launchers
8.1 General purpose
8.2 Incendiary and thermobaric
8.3 Special purpose
9 Recoilless rifles
10 Mortars
11 Anti-tank guided missiles
12 Man-portable air defense system
13 Landmines
14 See also
15 References
16 External links
Handguns[edit]
Revolvers[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Nagant M1895 7 shot revolver |
7.62×38mmR (7.62 mm Nagant) |
1895–present[1] still used by some police and security forces |
 A Nagant M1895 produced in 1941 by the Tula Arsenal with its 7.62×38mmR ammunition |
||
MP-412 REX Break-action revolver |
.357 Magnum (44.magnum) |
1993–present[citation needed] |
IZHMECH .357 Magnum Model 412 |
 MP-412 REX |
Pistols[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Tokarev pistol |
7.62×25mm Tokarev |
1930–present in use in some reserve forces |
TT-30 TT-33 1933 |
 Tokarev pistol |
|
Makarov pistol |
9×18mm Makarov |
1951–present still widely used by police, military and security forces |
IZh-70, IZh-71, MP-71 commercial variants:
|
 Makarov pistol |
|
PSM pistol |
5.45×18mm |
1973–present still issued to high ranking government officials, police, military & security forces |
IZh-75 (commercial) Baikal-441 (.25 ACP) |
 PSM pistol |
|
P-96 pistol |
9×19mm Parabellum (9×18mm Makarov) |
2000s–present |
P-96S (9×17mm) |
 P-96M |
|
GSh-18 |
9×19mm Parabellum |
2000–present one of the standard sidearms for all branches of Russian Armed Forces |
 GSh-18 |
||
MP-443 Grach Yarygin Pistol |
9×19mm Parabellum |
2003–present one of the standard sidearms for all branches of Russian Armed forces |
6P35 Yarygin (prototype) 9×19mm Parabellum MP-446 Viking (commercial) MP-446C (sporting variant) |
 MP-443 |
|
SR-1(Ru wiki only) |
9×21mm Gyurza |
2003–present sidearm utilized in limited numbers by the Spetsnaz |
SR-1M SR-1MP |
 SR-1M |
|
PL-14/15(Ru wiki only) |
9×19mm Parabellum |
Currently in prototype use |
PL-14 PL-15 PL-15K |
 PL-14 |
Special purpose[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Stechkin APS Stechkin automatic pistol select-fire machine-pistol |
9×18mm Makarov |
1951–present |
AO-44 / APB (variant with attaching silencer and steel wire stock) |
 |
|
SPP-1 underwater pistol |
4.5×39mm |
1971–present |
SPP-1M (updated model) |
 |
|
OTs-38 Stechkin silent revolver |
7.62×42mm SP-4 |
2002–present |
 |
||
PSS silent pistol also called MSS "Vul" ("wool" in English) |
7.62×42mm SP-4 |
1983–present replaced all previous noiseless pistols[2] |
PSS-2 (modernized; 7.62×45mm SP-16) |
 |
|
NRS-2 NR-2 (survival kit instead of pistol) |
7.62×42mm SP-4 |
1986–present |
NRS (initial variant; 7.62×35mm SP-3) knife / single-shot noiseless pistol designed to complement the PSS[3] |
 |
Submachine guns[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Bizon |
9×18mm Makarov |
1996–present succeeded by Vityaz-SN[citation needed] |
Bizon-2 (improved variant): 2 (9×18mm Makarov) 2B (configuration with attaching suppressor) 2-01 (9×19mm Parabellum) 2-02 (.380 ACP) 2-03 (integral suppressor) 2-07 (7.62×25mm Tokarev, box magazine) Bizon-3 (improved variant) |
 helical magazine; |
|
SR-2 Veresk |
9×21mm Gyurza |
1999–present |
SR-2M |
 |
|
Vityaz-SN[4] closed bolt |
9×19mm Parabellum |
1990s–present standard SMG for all branches of Russian military and police forces[5] |
Vityaz-SN |
 |
|
PP-2000 |
9×19mm Parabellum |
2008–present standard SMG for all branches of police forces[5] |
PP-2000 |
 |
|
PP-91 KEDR |
9x18mm Makarov |
1994–present used by parts of Ministry of Internal Affairs |
PP-71 (prototype) PP-90-01 (variant with integrated silencer) PP-9 "Klin" (1996-2002 for MVD 9x18mm PMM) |
 |
Special purpose[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
PP-90 Folding Submachine gun |
9x18mm Makarov |
1990s used by MVD |
 |
||
PP-90M1 Submachine gun |
9x19mm Parabellum |
1990s used by Spetsnaz |
|||
PPSh-41 General purpose submachine gun |
7.62x25mm Tokarev |
1941–1960 used by Red Army 1941–present (other Countries) 1941–1960 (Soviet Union) |
 |
||
OTs-02 Kiparis Submachine Gun |
9x18mm Makarov |
1972–1991 |
 |
Shotguns[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
RMB-93 Pump-action shotgun |
12-gauge shotgun |
1993 Used by Police of Russia and other security forces |
 |
||
Saiga-12 Automatic shotgun |
12-gauge shotgun , 16, 20, .410 gauge shotgun |
Late 1990s Used by Russian armed forces |
 |
||
MTs255 Revolver like shotgun |
12, 20, 28, .410 and 32-gauge shotgun |
1993 Used by Police of Russia and other security forces |
 |
||
KS-23 Special Carbine |
23mm bore shotgun |
1970–present,used by the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Border Guard Service |
|||
Molot Bekas-M Pump-action sporting shotgun |
12, 20, 28, .410 and 32-gauge shotgun |
1999 Used by Police of Russia and other security forces |
|||
TOZ-106 |
12 gauge |
1993 Used by Police of Russia and other security forces |
??? |
||
Vepr-12 Magazine fed semi-automatic shotgun |
7.62×39mm 12 gauge |
2003 Used by Police of Russia and other security forces |
 |
Rifles[edit]
Bolt-action[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Berdan rifle |
10.75×58 mmR; 24 gram paper-patched round nose lead bullet 7.62×54mmR |
1870–1895 |
|||
Mosin–Nagant "3-line rifle" "Mosin rifle" |
7.62×54mmR |
1891–present still used by some militia forces sniper rifle commonly used by police and military snipers |
1891 infantry 1891 dragoon 1891 cossack 1891/1910 1891/1930 1891/1952 KGB sniper 1907 carbine 1938 carbine 1944 carbine |
 Mosin–Nagant series of rifles |
|
SV-98 |
7.62×51mm NATO 7.62×54mmR .338 Lapua Magnum |
2003–present |
Modernized (1) |
 SV-98 |
|
VKS sniper rifle |
12.7×55mm STs-130 |
2004–present |
Some variants are in deployment |
 |
|
Orsis T-5000 |
7.62×51mm NATO (.308 Winchester) .300 Winchester Magnum .338 Lapua Magnum |
2017–present[6] |
Some variants are in deployment |
 |
Semi-automatic[edit]
- REDIRECT SVT-40
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SKS / Simonov self-loading carbine |
7.62×39mm |
1945–present still used by some police & militia forces, also used as ceremonial rifle |
 SKS |
||
Dragunov sniper rifle |
7.62×54mmR |
1963–present |
SVU (bullpup) SVDK (9.3×64mm) SVDS (folding stock): 590mm barrel (SVDS-D) |
 SVD |
Selective-fire[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
AK-47 / AK |
7.62×39mm |
1949–present replaced by AKM can still be found in armories. |
|
 AK-47 |
|
AKM modernized AK-47 |
7.62×39mm |
1959–present replaced by AK-74 still in use by police and militia forces |
|
 AKM |
|
AK-74 |
5.45×39mm |
1974–present replaced by AK-74M can still be found in large numbers |
|
 AK-74 |
|
AK-74M modernized AK-74 |
5.45×39mm |
1991–present current issue |
|
 AK-74M |
|
AN-94 / Nikonov Assault Rifle |
5.45×39mm |
1997–present used in limited numbers too expensive for general issue[7] |
 AN-94 |
||
AK-12 / AK-15 |
5.45×39mm 7.62×39mm |
Accepted into service in January 2018. In the process of replacing the AK-74 |
 AK-12 |
Special purpose[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
APS underwater automatic rifle |
5.66×39mm MPS |
1975 to present |
 APS |
||
AS Val silent assault rifle |
9×39mm |
1980s to present |
VSS Vintorez (sniper rifle) |
 AS Val |
|
9A-91 |
9×39mm |
1993 to present |
VSK-94 (sniper rifle) A-9 (9×19mm Parabellum) A-7.62 (7.62×25mm Tokarev) |
 9A-91 |
|
AK-9 carbine, sub- |
9×39mm |
2000s to present |
 AK-9 |
||
ASh-12.7 urban assault rifle |
12.7×55mm ASh-12.7 |
2010 to present |
 Ash-12.7 |
||
ADS amphibious |
5.45×39mm / 5.45×39mm PSP |
2013 to present |
Carbine A-91 (non-amphibious): |
 ADS |
Anti-material rifles[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
KSVK / ASVK / 6S8 / ASV Kord |
12.7×108mm |
1990s to present |
 ASVK |
||
OSV-96 folding barrel |
12.7×108mm |
1990s to present |
V-94 (early variant) |
 OSV-96 |
Machine guns[edit]
Squad automatic weapons (SAWs)[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
RPD / Light Machine Gun |
7.62×39mm |
1945 to present still used by special forces and militia forces |
 RPD Light Machine Gun |
||
RPK / Kalashnikov Light Machine Gun |
7.62×39mm |
1959 to present still used by police and militia forces |
AKM (assault rifle) S-108(-M), P-55 RPKS (folding stock) RPK(S)N RPK(S)L RPKM (modernized) RPK-203 (export variant) RPK-204 (7.62×51mm NATO) |
 RPK |
|
RPK-74 |
5.45×39mm |
1974 to present current issue |
AK-74 (assault rifle) RPKS-74 (folding stock) RPK(S)-74N: RPK-74M (modernized) RPK-201 (5.56×45mm NATO) |
 RPK-74 |
|
RPK-16 |
5.45×39mm |
2018 to present |
[8] |  RPK-16 |
General-purpose[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
PK machine gun Kalashnikov Machine Gun |
7.62×54mmR |
1961 to present |
PKM (modernized) PK(M)S (configuration PK(M)B (APC PKT(M) (tank variant) Pecheneg (rifle- |
 PK |
|
Pecheneg machine gun Kalashnikov Machine Gun |
7.62×54mmR |
2001 to present |
PKM (modernized) PK(M)S (configuration PK(M)B (APC PKT(M) (tank variant) Pecheneg (rifle- |
 PKM |
Heavy[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
KPV / Vladimirov Machine Gun |
14.5×114mm |
1949 to present |
PKP (infantry variant; not to be confused with Pecheneg machine gun) KPVT (vehicle-mounted) ZPU-1 / 2 / 4 (AA mounts) |
 KPV |
|
NSV Utyos / Nikitin– Sokolov–Volkov |
12.7×108mm |
1971 to present succeeded by Kord can still be found in large numbers |
NSVT (vehicle-mounted) Utyos-M (naval twin-mount) |
 NSV |
|
Kord can be fired |
12.7×108mm |
1998 to present |
 Kord |
Hand grenades[edit]
Fragmentation[edit]
| Weapon |
Weight |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
RGD-5 offensive fragmentation grenade |
310g |
1954 to present replaced by RGN can still be found in large numbers |
 RGD-5 |
||
RGO defensive fragmentation grenade |
530g |
1990s to present |
 RGO |
||
RGN offensive fragmentation grenade |
290g |
1990s to present |
 RGN |
Anti-tank[edit]
| Weapon |
Weight |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
RKG-3 shaped charge |
1,070 g |
1950 to present still stockpiled succeeded by RPG-18 rocket launcher |
RKG-3Ye (170 mm RHA) RKG-3YeM (220 mm RHA) |
 RKG-3 |
Grenade launchers[edit]
Stand-alone[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
RGS-50 |
50mm grenade |
1989 to present |
RGS-50M |
 |
|
RG-6 / 6G30 |
40mm caseless grenade (VOG-25M) |
1994 to present |
 RG-6 |
||
RGM-40 Kastet stand alone version of GP-30 with telescoping stock |
40mm caseless grenade (VOG-25M) |
late 1990s to present |
External: [1][2] |
||
GM-94 |
43mm grenade (VGM-93) |
2007 to present |
 GM-94 |
Attached[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Kalashnikov grenade launcher (cup type launcher)[9] |
uses special blank cartridge to launch standard RGD-5 hand-grenades also launches various riot control ammunition |
mid 1950s to present |
 Kalashnikov Grenade Launcher |
||
GP-25 Kostyor |
40mm caseless grenade (VOG-25M) |
1978 to present |
BG-15 Mukha initial variant GP-30 Obuvka: 1989 issue 2000 issue GP-30M GP-30U Granat (can be mounted on foreign rifles) GP-34 ([3]) |
 AK-74M with GP-25 |
Automatic grenade launchers[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
AGS-17 Plamya succeeded by |
30 mm VOG-17M / VOG-30 / GPD-30 |
1970s to present |
AGS-17M modernized AG-17M AG-17A (AP-30 |
 AGS-17 |
|
AGS-30 Atlant light automatic |
30 mm VOG-17M / VOG-30 / GPD-30 |
1995 to present |
TKB-722(K) prototype |
 AGS-30 |
|
AGS-40 Balkan automatic |
40mm caseless 7P39 grenades |
2017 to present |
 AGS-40 Balkan |
Rocket launchers[edit]
General purpose[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
Penetration |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
RPG-7 |
Anti-tank PG-7VL “Luch” 93mm, 2.6 kg, 1977 Tandem AT Thermobaric Fragmentation Outdated (AT) |
260 mm (V) 300 mm (VM) 400 mm (VS) 500 mm (VL) 750 mm (VR) |
1961 to present still used in large numbers succeeded by RPG-30 & RPG-32 |
RPG-7D paratrooper RPG-7N/DN RPG-7V RPG-7V1/D1 RPG-7V2/D2 RPG-7D3 |
 RPG-7 |
RPG-16 |
58x3mm HEAT |
300mm (RHA) |
1970s to 1990s |
||
RPG-26 Aglen (one-shot disposable launcher) |
72.5mm |
440 mm |
1985 to present |
RShG-2 (combined warhead (light)) |
 RPG-26 |
RPG-27 Tavolga (one-shot disposable launcher) medium AT |
105mm |
600 mm |
1989 to present |
RShG-1 |
External: [4], [5] |
RPG-29 Vampir for ranges of 500-800 |
105mm (AT, thermobaric) |
750 mm |
1989 to present |
 RPG-29 |
|
RPG-32 Hashim developed |
72.5 and 105mm |
650 mm |
2008 to present |
||
RPG-28 Klyukva (one-shot disposable launcher) heavy AT |
125mm |
~1000 mm |
2011 to present |
RMG multipurpose variant |
External: [6], [7], [8] |
RPG-30 Kryuk (one-shot disposable launcher) |
105mm |
600 mm |
2012 to present |
External: [9], [10] |
Incendiary and thermobaric[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
RPO Rys Incendiary rocket launcher replaced the flamethrower in Soviet service |
122mm |
late 1970s to present succeeded by |
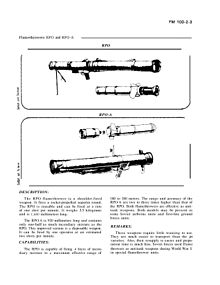 RPO |
|
RPO-A Shmel (one-shot disposable launcher) |
93mm |
late 1980s to present succeeded by |
RPO-A: thermobaric RPO-Z: incendiary RPO-D: smoke warhead RPO-M: 90mm reuseable launcher Bur: 62mm reusable launcher |
 RPO-A |
MRO-A (one-shot disposable launcher) |
72.5mm |
2002 to present |
MRO-A: thermobaric MRO-Z: incendiary MRO-D: smoke warhead |
 MRO |
| Varna (Incendiary rocket launcher) |
2005 to present[10] |
Special purpose[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Grad-P Light portable rocket system man-portable variant |
122mm 9M22M 10,800 / 15,000m |
1960s to present |
 Grad-P |
|
DP-61 Duel |
55mm depth charges |
late 1970s to present supplemented by |
MRG-1 Ogonyok: stationary variant with 7 launch tubes |
External: [11] |
DP-64 |
45mm depth charges |
1990 to present |
 |
Recoilless rifles[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SPG-9 Kopyo |
73mm |
1962 to present |
SPG-9D paratrooper variant SPG-9(D)M SPG-9(M)N/D(M)N |
 SPG-9 |
Mortars[edit]
| Weapon |
Caliber |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
82-BM-37 M37 M1937 PM37 |
82mm |
1936 to present replaced by the Podnos can still be found in large numbers |
M37M M41 M43 |
 |
2B14 Podnos |
82mm |
1980s to present |
 |
|
2B25 Gall suppressed mortar |
82mm |
2011 to present |
External: [12] |
Anti-tank guided missiles[edit]
| Weapon |
Missile |
Range |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
9K111 Fagot / AT-4 Spigot |
9M111 |
2,000m |
1970 to present |
9M111M |
 9K113 Konkurs missile system (launcher and missile) and a 9M111M Faktoriya missile in launch tube (standing) |
9M113 Konkurs / AT-5 Spandrel |
9M113 |
4,000m |
1974 to present |
9M113M |
 |
9K115-2 Metis-M / AT-13 Saxhorn-2 |
9M131 |
1,000m/ 2000m[11] |
1992–present |
Metis-M / Metis-M1 HEAT tandem warhead, Armor penetration behind ERA 900–950 mm[12] |
 |
9K135 Kornet / AT-14 Spriggan replaced 9M113 Konkurs |
9M133-1 9M133F-1 — 9M133M-2 9M133FM-2 9M133FMX |
5,500m — 8,000–10,000m |
1998 to present[13] |
Kornet-E (export) Kornet-D / EM |
 Kornet |
9K11-2 Malyutka-2 / AT-3D Sagger D modernized |
9M14-2 9M14-2M 9M14-2P 9M14-2F |
3,000m — min. 400m |
1999 to present |
Malyutka-2M |
External: [13] (Malyutka-2M) |
Man-portable air defense system[edit]
| Weapon |
Range |
Altitude |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Igla / SA-18 Grouse succeeded by Igla-S |
5,200m |
3,500m |
1981 to present |
Igla-1 (early variant; Igla-D (paratrooper Dzhigit (two-barrel |
 Igla |
Igla-S / SA-24 Grinch succeeded by 9K333 Verba |
6,000m |
3,500m |
2004 to present |
 Igla-S |
|
9K333 Verba |
8000m |
4,500m |
2014 to present |
 9K333 Verba |
Landmines[edit]
| Weapon |
Type |
In service |
Variants |
Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
POMZ |
Anti-personnel tripwire type fragmentation mine |
1945 to late 1960s |
POMZ-2 POMZ-2M |
 Yugoslav PMR-2A variant of POMZ anti-personnel mine, Balkans 1996 |
PMN mine |
Anti-personnel |
late 1950s to present |
PMN-1 PMN-2 PMN-4 |
 |
OZM |
anti-personnel bounding (Bouncing Betty) type |
OZM-3 OZM-4 OZM-72 |
 |
|
MON-50 |
anti-personnel directional (Claymore) type |
 |
||
MON-90 larger version of MON-50 |
anti-personnel directional (Claymore) type |
|||
MON-100 |
anti-personnel directional (Claymore) type |
 |
||
MON-200 larger version of MON-100 |
anti-personnel directional (Claymore) type, can also be used against light-skinned vehicles and helicopters |
|||
TM-57 mine |
anti-tank |
 |
||
TM-62 series of mines |
anti-tank |
TM-62M TM-62B TM-62D TM-62P TM-62T |
 |
|
TM-72 mine |
anti-tank stand-off magnetic fuze |
TM-89 |
See also[edit]
- List of equipment of the Russian Ground Forces
- List of Russian weaponry makers
- List of firearms
- List of bullpup firearms
- List of multiple barrel firearms
References[edit]
^ "Modern Firearms – Handguns – Nagant 1895". World.guns.ru. Retrieved 2010-07-20..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Пистолеты НИИ Точмаш". Retrieved 28 December 2016.
one-shot pistol
^ "-2". Retrieved 13 November 2014.
^ "Официальный сайт группы предприятий "ИЖМАШ"". 9 November 2011. Archived from the original on 9 November 2011. Retrieved 28 December 2016.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
^ ab "New guns for Russia's cops – so what? – In Moscow's Shadows". In Moscow's Shadows. Retrieved 13 November 2014.
^ https://rg.ru/2017/09/27/fsb-i-rosgvardiia-priniali-na-vooruzhenie-unikalnye-vintovki-tochnost.html
^ "Modern Firearms". Archived from the original on 14 September 2010. Retrieved 13 November 2014.
^ H, Hrachya. "Russia Adopts the RPK-16 Light Machine Gun". The Firearm Blog. Retrieved 2018-02-10.
^ Operator's Manual for AK-47 Assault Rifle Archived 2005-03-02 at the National and University Library of Iceland. Department of the Army
^ admin. "ОАО "Конструкторское бюро приборостроения" - Пехотный огнемет "Рысь"". Retrieved 28 December 2016.
^ admin. "KBP Instrument Design Bureau - Metis-M1". Retrieved 28 December 2016.
^ TulaKirill (21 August 2010). "anti-tank system METIS M-1 (противотанковый комплекс Метис - М1)". Retrieved 28 December 2016 – via YouTube.
^ "Kornet". Retrieved 28 December 2016.
External links[edit]
Categories:
- Weapons of Russia
- Lists of weapons
- Firearms of Russia
- Russian and Soviet military-related lists
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgPageParseReport":{"limitreport":{"cputime":"0.724","walltime":"0.941","ppvisitednodes":{"value":8620,"limit":1000000},"ppgeneratednodes":{"value":0,"limit":1500000},"postexpandincludesize":{"value":56510,"limit":2097152},"templateargumentsize":{"value":7595,"limit":2097152},"expansiondepth":{"value":11,"limit":40},"expensivefunctioncount":{"value":2,"limit":500},"unstrip-depth":{"value":1,"limit":20},"unstrip-size":{"value":33892,"limit":5000000},"entityaccesscount":{"value":0,"limit":400},"timingprofile":["100.00% 352.762 1 -total"," 43.54% 153.595 1 Template:Reflist"," 31.81% 112.219 11 Template:Cite_web"," 22.69% 80.048 87 Template:Flagcountry"," 19.75% 69.661 2 Template:Citation_needed"," 17.42% 61.441 2 Template:Fix"," 11.73% 41.379 87 Template:Flagcountry/core"," 9.86% 34.788 4 Template:Category_handler"," 8.26% 29.153 43 Template:Country_data_Russia"," 6.62% 23.358 1 Template:Dynamic_list"]},"scribunto":{"limitreport-timeusage":{"value":"0.133","limit":"10.000"},"limitreport-memusage":{"value":4825693,"limit":52428800}},"cachereport":{"origin":"mw1265","timestamp":"20190410044234","ttl":2592000,"transientcontent":false}}});});{"@context":"https://schema.org","@type":"Article","name":"List of modern Russian small arms and light weapons","url":"https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_modern_Russian_small_arms_and_light_weapons","sameAs":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q1015754","mainEntity":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q1015754","author":{"@type":"Organization","name":"Contributors to Wikimedia projects"},"publisher":{"@type":"Organization","name":"Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.","logo":{"@type":"ImageObject","url":"https://www.wikimedia.org/static/images/wmf-hor-googpub.png"}},"datePublished":"2006-08-03T22:29:23Z","dateModified":"2019-03-15T06:38:01Z","headline":"Wikimedia list article"}(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgBackendResponseTime":116,"wgHostname":"mw1240"});});wEBhgMVog4Xb7btYCkC3xj,c,wsQapf 6oJYdFHnID8MGenU